CopyRight 2009-2020 © All Rights Reserved.版权所有: 中国海关未经授权禁止复制或建立镜像
认识濒危爬行动物-幼发拉底斑鳖
作者:尹 羿1 汪 琳1 王继文2 任 彤1 张佳玮1
尹 羿1 汪 琳1 王继文2 任 彤1 张佳玮1
摘 要 幼发拉底斑鳖(Rafetus euphraticus),是一种濒危淡水鳖。为了持久保护幼发拉底斑鳖,本文对其分类地位、生物学特征及其保护现状进行总结概括。分析探讨该物种现有资源与保护现状,认识到幼发拉底斑鳖与东亚斑鳖是最为接近的物种。该物种活动范围在伊朗仅为西南部的淡水区域。近年来因战争不断,人们因开垦农田而修建水利大坝的行为,严重破坏了该物种的生存环境,导致该物种的数量正在不断下降。目前全球只有土耳其仅对该物种进行了研究。随着人类社会以及环境的变迁,幼发拉底斑鳖也成为濒危物种之一,要使幼发拉底斑鳖长期生存下去,还需对其种群加强研究,并加大国际间的保护以及区域合作。
关键词 幼发拉底斑鳖;淡水鳖;生活习性;分类;形态
Know Endangered Reptiles- Rafetus euphraticus
YIN Yi1 WANG Lin1 WANG Ji-Wen2 REN Tong1 ZHANG Jia-Wei1
Abstract Rafetus euphraticus is an endangered freshwater turtle. In order to substainably protect the euphratic softshell turtle, this article summarizes its classification status, biological characteristics and protection status. By analyzing the existing resources and protection status of this species, it is recognized that theeuphroditus and giant soft-shelled turtle are the closest species. The species is found in freshwater areas only in the southwest of Iran. In recent years, due to continuous wars and people building water conservancy dams for reclaiming farmland, the living environment of this species has been severely damaged, and the number of this species is declining. With the changes in human society and the environment, the Euphrates giant soft-shelled turtle has also become one of the endangered species. To ensure the long-term survival of the euphratic giant soft-shelled turtle, it is necessary to strengthen research on its populationand enhance international protection and regional cooperation.
Keywords Rafetus euphraticus; freshwater turtle; life habits; classification; morphology
幼发拉底斑鳖是一种中型淡水鳖,其生活的地理范围仅为土耳其、叙利亚、伊拉克和伊朗的幼发拉底河和底格里斯河盆地。随着人类社会发展以及环境的变化,幼发拉底斑鳖越来越少,1996年幼发拉底斑鳖被列入“濒危物种红色名录”中,现急需人类对其进行研究和保护。为了帮助海关口岸工作人员正确识别濒危动物,本文对濒危爬行动物幼发拉底斑鳖进行综述。
1 分类地位
作为一种爬行动物,幼发拉底斑鳖(Rafetus euphraticus)在形态学分类地位如下:龟鳖目鳖科(Trionychidae)斑鳖属(Rafetus Gray),与我国苏州园林中的斑鳖(Rafetus swinhoei)为同属。
最初将幼发拉底斑鳖命名为Testudo euphratica,后因标本来自底格里斯河即更名为Testudo rafcht。在鳖属物种制定了通用名Trionyx之后,又将其名字改为Trionyx euphraticus[1]。后期研究学者因注意到斑鳖的肺泡表面特征远不同于鳖属物种,即将斑鳖从鳖属Trionyx中移了出来,并起了个全新的属名Rafetus Gray。斑鳖属的明显特征为其腹甲只有两个胼胝体。斑鳖属是介于鳖属Trionyx和Potamochelys之间[2]。根据头骨和外壳的特征发现幼发拉底斑鳖(Rafetus euphraticus)与非洲鳖、滑鳖属(Apalone)的3个北美型物种,即A. ferox, A. mutica和A. spinifera[3],均是由同一个祖先进化而来[4]。Ihlow等人对来自土耳其、伊朗和伊拉克12个地区的31个幼发拉底斑鳖的两个线粒体基因,基因序列和ND4进行了测序,但没有发现不同地理株的较大差异[5]。
2 形态特征
幼发拉底斑鳖最显著的外部形态特征为鳖呈扁平状,背部较平(图1)。其背甲总长度(革质壳)在420mm~535mm之间。Siebenrock和Meylan 测量的骨板的最大长度为282 mm,目前有记录的骨板最大长度为351 mm [6]。研究发现,雄鳖和雌鳖背甲和从图2和图3可以看出,幼发拉底斑鳖的背甲呈长椭圆,表面光滑,无疣粒,前部肉质厚实。易辨认出骨盘的轮廓和缝合线。背甲为橄榄绿色,缀有一些大小不一的黄色斑点。部分个体整个背底色呈均匀的深棕色,极少数呈黑色(图3)。它的鼻部比例较三角鳖和中华鳖短而厚(图4)。成年的幼发拉底斑鳖前内侧有轻微的凹陷,幼体则没有[8]。
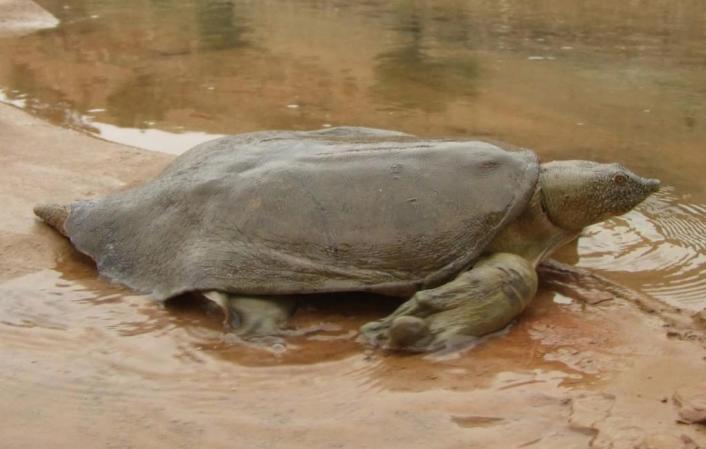

图1 伊朗胡齐斯坦省Balarood河的幼发拉底斑鳖
Fig.1 Rafetus euphraticus in Balarood River, Khuzestan Province, Iran. Photo by Hanyeh Ghaffari
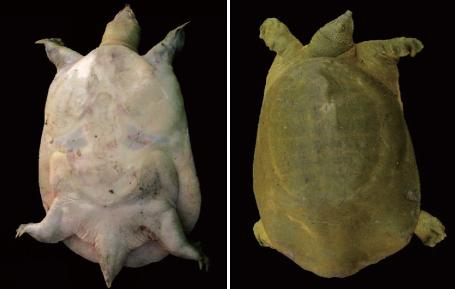
图2 来自伊朗胡齐斯坦省的Karkheh湖坝的幼发拉底斑鳖
Fig.2 Rafetus euphraticus from Karkheh Lake Dam, Khuzestan Province, Iran. Photos by Hanyeh Ghaffari
刚孵化的小鳖甲背呈椭圆形,有纵向排列的小凸起,小凸起没有延伸到甲背后缘,但是随着年龄的增长,甲背会变得光滑,小凸起也会逐渐消失。甲背呈橄榄灰色,头部外侧的斑点会延伸到颈部,数量明显多于头部和甲背的光斑[9]。刚孵化的龟甲颜色(图5)为砂灰色至淡黄色。

图3-1 来自伊拉克Hanyeh Ghaffari. Bottom的幼发拉底斑鳖
Fig.3-1 Rafetus euphraticus from Dukan Lake, Sulaimani, Iraq. Photo by Hanyeh Ghaffari. Bottom

图3-2 来自土耳其Saray-Birecik, Sanliurfa的幼发拉底斑鳖
Fig.3-2 Rafetus euphraticus from Saray-Birecik, Sanliurfa, Turkey. Photo by Mehmet Atatür.
3 地理分布与生活习性
幼发拉底斑鳖的分布范围仅限于土耳其、叙利亚、伊拉克和伊朗的幼发拉底河和底格里斯河流域 [10]。其中该物种在伊朗的活动范围仅在该国西南部的胡齐斯坦省的河流中。

图4 伊朗胡齐斯坦省地区的成年幼发拉底斑鳖
Fig.4 Adult Rafetus euphraticus from Khuzestan Province, Iran. Photo by Hanyeh Ghaffari

图5 来自伊朗胡齐斯坦省迪兹河的幼发拉底斑鳖幼体
Fig.5 Hatchling Rafetus euphraticus from Dez River, Khuzestan Province, Iran. Photos by Barbod Safaei-Mahroo
根据少量的文献所得知,幼发拉底斑鳖喜欢栖息在相对平浅的淡水区域,包括河流、小溪、池塘、湖泊、水库、沼泽地,甚至是城市附近的人工运河(图6)。幼发拉底河和底格里斯河因其河道有浅水回流、季节性池塘和湿地,流域面积广阔,光照充足以及河内丰富的动植物,被该物种所喜爱。成年和幼年的幼发拉底斑鳖对于栖息地的选择不太相同。成年的幼发拉底斑鳖喜欢在水较深的支流(水深2m左右)中栖息,而幼年的幼发拉底斑鳖则更喜欢在水温较高,易捕食到食物的水坑生活。相对广阔的深水域,幼发拉底斑鳖则更喜欢栖息在有植被的海岸区域。因为海岸的植被可做为保护其筑巢、产卵的重要屏障使其免受干扰而得以休养生息。幼发拉底斑鳖在春、夏、秋季活动较为频繁。它是一种选择性杂食动物,它们通常会因环境的变换而伺机捕捉植物、鱼类或是河内腐蚀物等。幼发拉底斑鳖的产卵期大约在每年4月底到6月初。其卵呈球形,平均直径范围为大约在28.2 ~ 29.2 mm。

图6 伊朗库泽斯坦北部的幼发拉底斑鳖栖息地
Fig.6 Rafetus euphraticus habitats in northern Khuzestan, Iran. Photos by Barbod Safaei-Mahroo
4 资源现状与保护利用
当地因战争以及人为因素的破坏,严重影响到了幼发拉底斑鳖的生存条件。河流内建造的防洪发电大坝引发了水位和温度变化。导致河流内动物及植被的数量被改变,而这些变化强烈地影响了幼发拉底斑鳖种群的生存。此外,该物种还受到农药、化肥、石油、垃圾以及工业化学品水污染的影响。人为因素的改变都将导致幼发拉底斑鳖的生存环境进一步被破坏,甚至可能还会增加局部灭绝的可能性。
在幼发拉底河和底格里斯河的许多支流,夏季干旱时水位下降得很快,人们用河内的水对农田进行灌溉,以致于河床干涸,幼发拉底斑鳖被困在这些地方的小水塘里,其生态环境处于崩溃状态。
在外来物种入侵方面,中华鳖被非法带入到伊朗后成为幼发拉底斑鳖的竞争对手。在伊朗的德黑兰和阿瓦士市中有宠物店出售中华鳖幼体的情况[11]。当地人们因一时好奇购买后进行饲养,当好奇心消失殆尽后会将圈养的中华鳖放生到附近的淡水栖息地中。又因中华鳖的习性、特征与幼发拉底斑鳖非常接近,最终导致两者在日趋恶劣生存环境中相互竞争。除此以外,由于伊拉克各种战争、政治冲突、石油开发以及肆意捕捞鱼群等现象也都威胁着幼发拉底斑鳖的生存环境。
保护措施:1996年国际自然保护联盟(IUCN)公布的濒危物种红色名录(IUCN 2015年发布)中,幼发拉底斑鳖被列为濒危物种。IUCN/ SSC陆龟和淡水龟专家组根据2011年的评估草案(TTWG 2014)将其列为濒危物种。在伊朗,法律禁止杀害或捕获幼发拉底斑鳖。伊朗环境最高委员会已立法规定,对捕获或杀害幼发拉底斑鳖处以5000万里亚尔(相当于1400美元)的罚款。该物种被列为濒危野生动植物种国际贸易公约附录II中,即濒临灭绝物种,如对其贸易不严加管理,就可能面临被灭绝的危险。
对幼发拉底斑鳖当前的研究包括基因结构、生境适宜性、筑巢、活动范围、栖息地选择以及解剖学[1, 5-7,12](Ahranjani等[1],2016;Ghaffari等[6,7,9],2013,2014,2015;Ihlow等[7],2014年;Biricik[12],2011)。2009~2012年,帕尔斯爬虫学家研究所与联合国开发计划署小额赠款项目资助开展了一项保护胡齐斯坦省幼发拉底斑鳖种群的保护计划。该项目的目的在于提高当地人们保护该物种的意识,并强调对幼发拉底斑鳖采取保护措施的必要性。
5 结论
目前,幼发拉底斑鳖在全球有4处保护区域,迪兹国家公园及保护区、卡赫赫国家公园及保护区、哈瓦-阿齐姆保护区以及沙德根野生动物保护区。由于适宜该物种生存的栖息地急剧减少,人们应加强该物种的区域性保护,保护其繁殖区域不受外界干扰。定期监测该物种在每个国家分布的种群规模及趋势也非常重要。根据幼发拉底斑鳖列入濒危物种世界自然保护联盟红色名录这一情况,制定或修改保护该物种的法律法规,开展实施保护计划,提高人们对幼发拉底斑鳖的保护。
【该文经 CNKI 学术不端文献检测系统检测,总文字复制比为0.1%。】
参考文献
[1] AhrAnjAni, B.A., ShojAei, A. Anatomical, radiographical and computed tomographic study of the limbs skeleton of the Euphrates soft shell turtle (Rafetus euphraticus)[J]. Veterinary Research Forum, 2016, 7(2): 117-124.
[2] TucK, r.g., jr. Additional notes on Iranian reptiles in the United States National Museum Collection[M]. Bulletin of the Maryland Herpetological Society, 1973, 9: 13-14.
[3] BuhlMAnn, K.A. AKre, T.S.BiverSon, A global analysis of tortoise and freshwater turtle distributions with identification of priority conservation areas[J]. Chelonian Conservation and Biology.2009, 8(2): 116-149.
[4] ghAffAri, TASKAvAK, and KArAMi, M. Conservation status of the Euphrates softshell turtle, Rafetus euphraticus, in Iran[J]. Chelonian Conservation and Biology, 2008, 7(2): 223-229.
[5] GhAffAri,h., pluMMer, M.v. Notes on a nest and emergence of hatchlings of the Euphrates softshell turtle (Rafetus euphraticus) at the Dez River, Iran[J]. Chelonian Conservation and Biology, 2013, 12: 319-323.
[6] GhAffAri, SAfAei-MAhroo, And rödder, D. Home range and habitat selection of the endangered Euphrates softshell turtle Rafetus euphraticus in a fragmented habitat in southwestern Iran[J]. Chelonian Conservation and Biology, 2014, 13(2): 202-215.
[7] Ihlow, F., ahMadzadeh, F., GhaFFari, h., Taşkavak, e., harTMann, T., eTZBAuer, c., And rödder, D. Assessment of genetic structure, habitat suitability and effectiveness of reserves for future conservation planning of the Euphrates soft-shelled turtle Rafetus euphraticus [J]. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 2014, 24: 831-840.
[8] NTure irAq. Key Biodiversity Areas of Iraq. Sulaimani[M], Iraq: Tablet House Publishing, 2016, 327 pp.
[9] SAfAei-MAhroo, B., ghAffAri, h., fAhiMi, h., BrooMAnd, S.,yAZdAniAn, M., nAjAfi MAjd, e., hoSSeiniAn youSefKhAni, S.S., reZAZAdeh, e., hoSSeinZAdeh, M.S., nASrABAdi, r., rAjABiZAdeh, M., MAShAyeKhi, M., MoTeShArei, A., nAderi, A., And KAZeMi, S.M. The herpetofauna of Iran[J]. checklist of taxonomy, distribution and conservationstatus. AsianHerpetologicalResearch, 2015, 6(4): 257-290.
[10] TTwg (TurTle TAxonoMy worKing group) . Turtles of the world, 7th edition: annotated checklist of taxonomy, synonymy, distribution with maps, and conservation status. In: Rhodin, A.G.J., Pritchard, P.C.H., van Dijk,. Conservation Biology of Freshwater Turtles and Tortoises: A Compilation Project of the IUCN/SSC Tortoise and Freshwater Turtle Specialist Group[C]. Chelonian Research Monographs .2014, 5(7): 329-479.
[11] TucK, r.g., jr. Amphibians and reptiles from Iran in the United States National Museum Collection. Bulletin of the Maryland Herpetological Society[C]. 1971, 7: 48-86.
[12] Biricik, M. and Turğa, S. Description of an Euphrates softshell turtle (Rafetus euphraticus) nest from the Tigris River (SE Turkey)[J]. Salamandra ,2011, 47: 99-102.
(文章类别:CPST-C)







